Exploring New Directions in Regulatory Affairs through Integration of Cutting-Edge Technological Innovations
Tech Innovations on a global scale, the Life Sciences and Pharmaceutical sector continually integrates advanced technologies and innovative therapies to enhance the quality of medicines, medical devices, and biologics. However, existing regulatory frameworks struggle to keep pace with these evolving methods of diagnosis and treatment. To ensure the availability of high-quality medications and diagnostics for patients, regulatory agencies are proactively identifying and implementing new policies or updating current guidelines to effectively evaluate novel therapeutics and devices, thereby ensuring their safety and effectiveness.
The emergence of a global pandemic has further underscored the need for regulatory bodies to swiftly assess and approve safe products to combat COVID-19. Adapting drug development processes, conducting pre- and post-marketing clinical studies, managing manufacturing, supply chain logistics, and distribution in the altered business landscape require regulatory bodies to adopt alternative perspectives. They are actively addressing various emerging challenges faced by the industry and issuing corresponding guidelines to navigate these processes effectively.
Top of Form
As health authorities introduce fresh policies and directives, organizations may find themselves needing to reassess their regulatory affairs setup and operations, adapting them to comply with evolving regulations. Throughout this journey, they may encounter numerous challenges at different stages of the process. What novel trends lie on the horizon, and how might they impact the management of regulatory affairs for stakeholders? Delve into the specifics in our in-depth exploration of ‘Emerging Trends in Regulatory Affairs Through Embracing Latest Technological Innovations.’
Present obstacles in regulatory affairs for sponsors Tech Innovations
As the pharmaceutical industry advances in its efforts to provide improved quality medicines, sponsors continue to encounter various challenges in both process and technology adoption.
Process Challenges:
- Securing regulatory approval for a drug remains a time-consuming endeavor, particularly exacerbated during the pandemic. This results in escalated costs, a more intricate supply chain, and necessitates refined systems to uphold regulatory compliance.
- Keeping pace with evolving regulatory requirements is imperative yet demanding.
- Collaboration among multiple stakeholders has become increasingly challenging due to COVID-19 restrictions, compounded by uneven digital connectivity, resulting in communication gaps.
- Sponsors must provide sufficient evidence from in vitro studies to ensure the safety of proposed clinical trials.
- Marketing authorization applications (MAAs) necessitate comprehensive evidence encompassing the drug’s chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC), as well as preclinical studies on pharmacology, pharmacokinetics (PK), and ADME.
- Creating and maintaining country-specific versions of information is vital to fulfill regional health authorities’ requirements.
- Maintaining distinct manufacturing processes for the same product to ensure availability can lead to inventory segmentation and potential errors concerning production and regulatory compliance.
- Managing GxP inspections, crucial for submission approval, requires diligent oversight.
Facing technical obstacles:
Keeping up with the rapidly evolving landscape of modern technology involves navigating through frequent updates and utilizing various electronic devices and software tools, which can often pose challenges.
With emerging methods and strategies, existing study frameworks may not suffice in assessing the effectiveness of new drugs.
The ongoing progression of medical research necessitates the development of innovative techniques and approaches to effectively evaluate emerging medical studies.
Emerging Regulatory Strategies to Streamline Review Procedures Tech Innovations
The conventional trajectory of clinical development within pharmaceutical companies has encountered significant disruption with the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. This global health crisis has upended traditional methods of drug testing, necessitating a reevaluation of established practices. As the pandemic continues to impose constraints on the scope of clinical studies, pharmaceutical manufacturers must proactively explore alternative avenues and embrace innovative approaches facilitated by accelerated digital adoption. By integrating the following strategies, pharma companies can reimagine the landscape of clinical development.
Adopting Real World Evidence (RWE) Tech Innovations
In recent years, there has been a growing trend among manufacturers to utilize real-world evidence (RWE) in the development of clinical trial designs and observational studies, paving the way for innovative treatment strategies. An illustrative example occurred in 2017 when the FDA utilized RWE to expand the application of Edwards Life Sciences’ transcatheter aortic valve replacement device for valve-in-valve procedures.
This marked a significant milestone as it represented the FDA’s first approval based on RWE, obviating the need for new clinical trial data. The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of RWE, offering a means to expedite the evaluation of new treatments within a matter of weeks or months, contrasting with the prolonged timelines associated with traditional randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
Embracing Virtual-First Approaches
Given the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, numerous organizations are increasingly embracing virtual trial methodologies, particularly for interventions deemed low-risk and well-understood (such as exploring new indications for existing therapies targeting chronic diseases). Both the US FDA and the EMA have provided guidance endorsing the adoption of virtual trials. One of the primary advantages of virtual trials lies in their ability to swiftly recruit specific patient cohorts, regardless of their geographical location, thereby offering unparalleled flexibility. Industry experts contend that virtual trials are notably more time-efficient, with patient recruitment taking as little as 4 months compared to the traditional timeline of 7 months.
Embracing Contemporary Technological Advancements
Incorporating computers, mobile gadgets, and wearable biosensors allows for the collection and retention of extensive health-related information. This reservoir of data offers the opportunity to improve the planning and execution of clinical trials and research endeavors in healthcare settings. Furthermore, with the progression of advanced analytical tools, we stand prepared to dissect this data and utilize the findings to advance medical innovations and streamline the approval procedures.
Utilizing Real-World Data (RWD)
Real-world data (RWD) offers insights into patients’ health statuses, sourced from various channels including:
- Electronic health records (EHRs)
- Claims and billing records
- Product and disease registries
- Patient-generated data
- Information collected from mobile devices.
In 2016, the FDA began considering real-world evidence to address off-label drug usage in approvals. Unlike controlled clinical studies where patients are closely monitored in controlled environments, the FDA evaluates clinical data to compare treatments or placebos.
However, real-world scenarios introduce data variability due to uncertainties in patients’ daily activities and exposures. RWD plays a crucial role in monitoring post-market safety, adverse events, and guiding regulatory decisions.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine, originally devised to support healthcare facilities, utilizes electronic communication to deliver clinical services to patients without necessitating in-person visits. Its technology facilitates various medical tasks remotely, such as follow-up appointments, chronic condition management, medication oversight, specialist consultations, and other clinical services via secure video and audio connections. Moreover, telemedicine applications can be expanded to effectively oversee clinical trials and collect adverse event data.
By integrating telemedicine apps with biosensors, researchers can gather and monitor subject data, allowing for continuous remote monitoring without confining individuals to healthcare facilities. This approach minimizes subjects’ exposure to external factors, thereby enhancing study conditions. Additionally, eliminating the need for subjects to travel ensures that appointments and follow-ups remain consistent and efficient. These benefits translate into both revenue and time savings, underscoring the importance of thoughtful planning and execution by study designers.
Pragmatic Clinical Trials (PCTs)
The need for rapid evidence gathering in COVID-19 treatment trials has spurred the adoption of Pragmatic Clinical Trials (PCTs) as a more efficient approach. These trials focus on optimizing the current research landscape and streamlining regulatory processes to swiftly generate timely evidence, particularly crucial during pandemics, aiding in more informed drug approvals.
PCTs, characterized by their patient-centric and outcome-driven nature, aim to assess the comparative benefits and risks of therapeutic interventions, offering insights for both clinical practice and policymaking. Leveraging electronic health records (EHR), they employ innovative designs to expedite the evaluation of significant clinical inquiries.
By assessing intervention effectiveness in real-world settings, PCTs provide valuable insights into how treatments perform outside controlled environments. With minimal exclusion criteria and interventions integrated into routine care by diverse clinicians, these trials prioritize external validity to enhance generalizability.
Today, the feasibility of PCTs is enhanced by the extensive collaboration within research networks and the integration of health systems, facilitated by unified EHR systems across hospitals and clinics.
Advantages of Pragmatic Clinical Trials:
Pragmatic Clinical Trials (PCTs) employ electronic health record (EHR)-based methods for automated screening and randomization, streamline consent procedures, and integrate follow-up assessments into regular clinic visits.
By leveraging machine learning and advanced language processing tools, endpoint determination can be achieved via automated periodic review of EHR data, facilitating interim analysis and safety monitoring.
The ease of data collection inherent in PCTs facilitates adaptive trial design, enabling the adjustment of tested interventions and sample size calculations as needed.
Conducting trials in real-world settings yields results that are more broadly applicable, making them easier to implement in clinical practice.
The reduced per-patient cost associated with PCTs allows for larger sample sizes, thereby minimizing protocol deviations.
Furthermore, unlike traditional Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs), PCTs with large sample sizes can evaluate multiple interventions and outcomes, including patient-centered metrics like quality of life and health service delivery measures such as efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics refers to the analysis of vast amounts of data generated within hospitals and clinics on a daily basis, characterized by increased velocity and variety. In recent times, another aspect, known as Veracity, has gained significance, indicating the quality and reliability of the data.
The utilization of big data holds the potential to streamline intricate business processes, leading to improved decision-making and strategic initiatives. Particularly, its impact on the pharmaceutical and life sciences sector is profound.
In clinical trials, big data plays a pivotal role in patient recruitment by tracking relevant genetic information and disease statuses. It aids researchers in predictive modeling for drug discovery, potentially accelerating the development of new medications. Moreover, in precision medicine, big data facilitates a deeper understanding of patients’ genetic makeup, environmental influences, and behavioral patterns, thereby enhancing diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Furthermore, integrating big data into research and development endeavors within the pharmaceutical industry offers businesses a comprehensive understanding of various drugs and their developmental trajectories.
The utilization of big data in the pharmaceutical industry presents a multitude of advantages across various domains. Key benefits encompass:
- Real-world Patient Data Capture: Acquiring authentic patient data from real-world scenarios.
- Enhanced Disease Understanding: Improved comprehension of diseases and their intricacies.
- Optimized Clinical Trials, Products, and Treatments: Facilitating the design of clinical trials, products, and treatment methodologies for enhanced efficacy.
- Cost Reduction, Quality Enhancement, and Efficiency: Streamlining operations to reduce costs while simultaneously enhancing quality and efficiency.
- Tailored Drug Development: Customizing the development of drugs to suit specific needs and requirements.
- Forecasting Disease Trends and Medical Projections: Utilizing data analytics to predict disease trends and make informed medical forecasts.
- Early Detection of Severe Adverse Events: Early identification of severe adverse events through data analysis.
- Assessment of Drug Comparative Effectiveness: Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of different drugs.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) encompasses various technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and Natural Language Processing (NLP). Its purpose is to mimic human abilities in analyzing and understanding complex medical data.
In contrast to conventional analytics and clinical decision-making methods, AI offers enhanced performance. Through continuous interaction with training data, learning algorithms enable humans to gain unparalleled insights into diagnostics, treatment processes, variability in treatments, and patient results. This capability ultimately enhances the accuracy and precision of outcomes by improving data quality.
The pharmaceutical sector is experiencing substantial benefits from AI-driven enhancements in research and development (R&D), manufacturing processes, as well as sales and marketing strategies.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers numerous advantages across various domains:
- AI’s deep learning algorithms enable swift and accurate diagnosis of severe illnesses, leading to prompt therapeutic intervention with more precisely targeted medications.
- Technology companies operating in pharmaceuticals stand to gain auxiliary benefits as algorithms for target identification and clinical-trial recruitment become integral to research and development processes.
- AI enhances patient accessibility to healthcare services.
- Improved patient screening and records management are facilitated by AI systems.
- AI is progressing towards realizing the concept of “virtual biopsies” and advancing the field of radiomics. These innovations utilize image-based algorithms to characterize tumor phenotypes and genetic properties.
- By automating routine clinical documentation processes, AI alleviates the burden associated with electronic health record (EHR) usage.
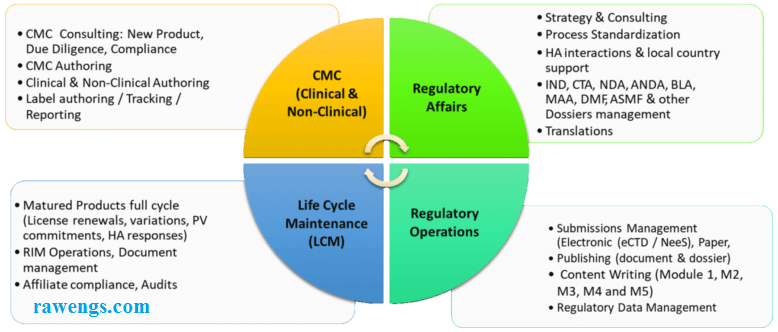
How Techsol’s rCoE (Regulatory centre of excellence) ensures adoption of industry best practices in the client regulatory affairs department?
Techsol’s Regulatory Center of Excellence (rCOE) is dedicated to ensuring that our clients’ regulatory affairs departments adhere to industry best practices. We are committed to keeping our clients informed about the latest developments in various GxP and Data Privacy regulations. Through thorough evaluation of business process risks, we propose optimal best practices for implementing enterprise-wide compliance measures. Leveraging our extensive regulatory experience in GxP, Techsol has assisted numerous global companies in formulating strategies and adapting continuously from a compliance standpoint, spanning from development to commercialization.
Our comprehensive range of services includes:
- Facilitation of CTD/eCTD Submissions
- Coordination of CTAs Submissions
- Review and compilation of Product Registration dossiers (such as NDA/MAA/ANDA, IND/CTA, DMF)
- Management of Life Cycle including Annual Reports, Variations, Renewals, and Safety Reports
- Handling 510(k) Submissions
- Managing PMA Submissions
- Preparation and review of T-License, Import/Export dossiers
- Response preparation for regulatory authorities or review of deficiency responses
- eCTD Submissions for IND/CTA, NDA/MAA, ANDA
- Acting as Regulatory Agency Liaison
- Compiling DMFs for Submission to EU and USFDA in CTD format
- Providing GMP compliance services for APIs and finished manufacturing facilities
- Offering AI model development and platform services including ML, NLP, and RPA
- Managing Big Data effectively.
Through these services, Techsol’s rCOE ensures that our clients are equipped to navigate the complexities of regulatory compliance while staying abreast of industry best practices.