eCTD-module-3-drug-products Understanding the 5 Modules of Regulatory Affairs in eCTD/CTD/ACTD Format-Part 2
eCTD-module-3-drug-products Module 3 drug products
eCTD-module-3-drug-products Module 3 of a regulatory submission for a drug product plays a crucial role in the approval process, as it includes information about the product’s quality, safety, and efficacy. In this response, we will explore the regulatory requirements of Module 3 and provide an overview of the information that is typically included in this section of a regulatory submission.
Regulatory Requirements for Module 3: eCTD-module-3-drug-products
The specific regulatory requirements for Module 3 vary depending on the region and type of submission. In the United States, for example, Module 3 is typically part of a New Drug Application (NDA) or Biologics License Application (BLA) submission to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In the European Union (EU), it is part of a Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) submission to the European Medicines Agency (EMA). However, despite these differences, there are several common regulatory requirements for Module 3 across regions and submission types.
One of the main regulatory requirements for Module 3 is the inclusion of data on the drug substance. This includes information on the chemical structure, purity, and characterization of the drug substance, as well as the methods used to synthesize and manufacture it. In addition, the drug substance data should include information on any impurities, degradation products, and residual solvents that may be present, and the methods used to control their levels.
Another important regulatory requirement for Module 3 is the inclusion of data on the drug product formulation and manufacturing process. This includes information on the composition of the drug product, as well as the methods used to manufacture it, including the manufacturing process steps, in-process controls, and the equipment used. The manufacturing process data should also include information on the control and monitoring of critical process parameters, and the methods used to ensure batch-to-batch consistency.
In addition to the drug substance and drug product data, Module 3 must also include information on the analytical methods used to evaluate the product. This includes information on the validation and qualification of the analytical methods, as well as the methods used to test the drug substance and drug product for quality attributes such as identity, purity, potency, and stability. The analytical methods data should also include information on the analytical specifications used to set acceptance criteria for these quality attributes.
Another critical component of Module 3 is the inclusion of stability data. This includes data on the stability of the drug substance and drug product under various conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and light. The stability data should demonstrate that the drug product will remain stable and retain its quality attributes over its intended shelf life.
Finally, Module 3 may also include information on clinical trial results, packaging, labeling, and product information. Clinical trial results data may include information on the design and conduct of clinical trials, as well as the results of those trials, such as efficacy and safety data. Packaging and labeling data should include information on the materials used, the design of the packaging, and the information included on the label, such as dosing information, warnings, and precautions. Product information may include instructions for use, patient information leaflets, and other materials that are intended to provide information to patients and healthcare professionals about the drug product.
Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for the successful approval of drug products by regulatory agencies worldwide. The regulatory requirements are in place to ensure that drug products are safe, effective, and of high quality. In this response, we will explore the importance of compliance with regulatory requirements in drug products.

The Role of Regulatory Agencies:
Regulatory agencies play a critical role in ensuring that drug products are safe and effective. They are responsible for reviewing drug product submissions and evaluating the data to determine if the product meets regulatory requirements. Regulatory agencies also monitor drug products that are on the market to ensure that they continue to meet these requirements.
Regulatory agencies have established guidelines and regulations that manufacturers must follow when developing drug products. These guidelines cover a wide range of topics, including clinical trials, manufacturing processes, quality control, and labeling. Compliance with these guidelines is essential for the approval of a drug product.
Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP):
One of the most critical regulatory requirements for drug products is compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP). GMP is a set of guidelines that regulate the production and quality control of drug products. The guidelines cover everything from the design of the manufacturing facility to the testing of the finished product.
GMP ensures that drug products are produced consistently and are of the required quality. Compliance with GMP guidelines is essential for the approval of drug products. Failure to comply with GMP can result in the rejection of a drug product submission or the withdrawal of a product from the market.
Compliance with Clinical Trial Requirements:
As other essential regulatory requirement for drug products is compliance with clinical trial requirements. Clinical trials are used to test the safety and efficacy of a drug product. Regulatory agencies require that drug products undergo clinical trials before they can be approved for use.
Clinical trials must be conducted according to specific guidelines and regulations. The trials must be designed and conducted in a way that ensures the safety of the participants and the validity of the results. Compliance with these requirements is critical for the approval of a drug product.
Compliance with Labeling Requirements:
Drug product labeling is another critical area for regulatory compliance. Drug product labeling must include information about the drug product, including its indications, dosage, contraindications, and side effects. The labeling must be accurate and easy to understand.
Regulatory agencies review drug product labeling to ensure that it is clear and accurate. Failure to comply with labeling requirements can result in the rejection of a drug product submission or the withdrawal of a product from the market.
The Consequences of Non-Compliance:
The consequences of non-compliance with regulatory requirements can be severe. Failure to comply with regulatory requirements can result in the rejection of a drug product submission or the withdrawal of a product from the market. These outcomes can be costly and time-consuming for manufacturers.
In addition to the financial consequences, non-compliance with regulatory requirements can also damage the reputation of the manufacturer. A product that is rejected by regulatory agencies or withdrawn from the market due to non-compliance can damage the manufacturer’s credibility and lead to a loss of consumer confidence.
Conclusion:
Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for the successful approval of drug products by regulatory agencies. Regulatory agencies have established guidelines and regulations that manufacturers must follow when developing drug products. Compliance with these guidelines is critical for the approval of a drug product.
The consequences of non-compliance with regulatory requirements can be severe. Failure to comply with regulatory requirements can result in the rejection of a drug product submission or the withdrawal of a product from the market. These outcomes can be costly and time-consuming for manufacturers and can damage the manufacturer’s reputation. Therefore, compliance with regulatory requirements should be a top priority for manufacturers developing drug products.
Drug Product Regulatory Requirements.
Module 3 of a regulatory submission for a drug product typically includes information about the product’s quality, safety, and efficacy. The specific regulatory requirements vary depending on the region and type of submission, but generally include data on the drug substance, drug product formulation and manufacturing process, analytical methods used to evaluate the product, stability data, and clinical trial results. In addition, Module 3 may also include information on packaging, labeling, and product information. Compliance with relevant regulations and guidelines is crucial for successful regulatory approval of a drug product.
Module 3 of a regulatory submission for a drug product plays a crucial role in the approval process, as it includes information about the product’s quality, safety, and efficacy. In this response, we will explore the regulatory requirements of Module 3 and provide an overview of the information that is typically included in this section of a regulatory submission.
Regulatory Requirements for Module 3:
The specific regulatory requirements for Module 3 vary depending on the region and type of submission. In the United States, for example, Module 3 is typically part of a New Drug Application (NDA) or Biologics License Application (BLA) submission to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In the European Union (EU), it is part of a Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) submission to the European Medicines Agency (EMA). However, despite these differences, there are several common regulatory requirements for Module 3 across regions and submission types.
One of the main regulatory requirements for Module 3 is the inclusion of data on the drug substance. This includes information on the chemical structure, purity, and characterization of the drug substance, as well as the methods used to synthesize and manufacture it. In addition, the drug substance data should include information on any impurities, degradation products, and residual solvents that may be present, and the methods used to control their levels.
Another important regulatory requirement for Module 3 is the inclusion of data on the drug product formulation and manufacturing process. This includes information on the composition of the drug product, as well as the methods used to manufacture it, including the manufacturing process steps, in-process controls, and the equipment used. The manufacturing process data should also include information on the control and monitoring of critical process parameters, and the methods used to ensure batch-to-batch consistency.
In addition to the drug substance and drug product data, Module 3 must also include information on the analytical methods used to evaluate the product. This includes information on the validation and qualification of the analytical methods, as well as the methods used to test the drug substance and drug product for quality attributes such as identity, purity, potency, and stability. The analytical methods data should also include information on the analytical specifications used to set acceptance criteria for these quality attributes.
Another critical component of Module 3 is the inclusion of stability data. This includes data on the stability of the drug substance and drug product under various conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and light. The stability data should demonstrate that the drug product will remain stable and retain its quality attributes over its intended shelf life.
Finally, Module 3 may also include information on clinical trial results, packaging, labeling, and product information. Clinical trial results data may include information on the design and conduct of clinical trials, as well as the results of those trials, such as efficacy and safety data. Packaging and labeling data should include information on the materials used, the design of the packaging, and the information included on the label, such as dosing information, warnings, and precautions. Product information may include instructions for use, patient information leaflets, and other materials that are intended to provide information to patients and healthcare professionals about the drug product.
The Importance of Compliance with Regulatory Requirements:
Compliance with the regulatory requirements for Module 3 is crucial for successful regulatory approval of a drug product. Failure to meet these requirements can result in delays in the approval process or even the rejection of the submission.
One of the primary reasons that compliance is so important is that regulatory agencies use the information in Module 3 to evaluate the quality, safety, and efficacy of the drug product. For example, the data on the drug substance and drug product formulation and manufacturing process are used to evaluate the quality of the product and ensure that it is safe for patients to use. The stability data is used to
The Importance of Compliance with Regulatory Requirements in drug products
Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for the successful approval of drug products by regulatory agencies worldwide. The regulatory requirements are in place to ensure that drug products are safe, effective, and of high quality. In this response, we will explore the importance of compliance with regulatory requirements in drug products.
The Role of Regulatory Agencies:
Regulatory agencies play a critical role in ensuring that drug products are safe and effective. They are responsible for reviewing drug product submissions and evaluating the data to determine if the product meets regulatory requirements. Regulatory agencies also monitor drug products that are on the market to ensure that they continue to meet these requirements.
Regulatory agencies have established guidelines and regulations that manufacturers must follow when developing drug products. These guidelines cover a wide range of topics, including clinical trials, manufacturing processes, quality control, and labeling. Compliance with these guidelines is essential for the approval of a drug product.
Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP):
One of the most critical regulatory requirements for drug products is compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP). GMP is a set of guidelines that regulate the production and quality control of drug products. The guidelines cover everything from the design of the manufacturing facility to the testing of the finished product.
GMP ensures that drug products are produced consistently and are of the required quality. Compliance with GMP guidelines is essential for the approval of drug products. Failure to comply with GMP can result in the rejection of a drug product submission or the withdrawal of a product from the market.
Compliance with Clinical Trial Requirements:
Another essential regulatory requirement for drug products is compliance with clinical trial requirements. Clinical trials are used to test the safety and efficacy of a drug product. Regulatory agencies require that drug products undergo clinical trials before they can be approved for use.
Clinical trials must be conducted according to specific guidelines and regulations. The trials must be designed and conducted in a way that ensures the safety of the participants and the validity of the results. Compliance with these requirements is critical for the approval of a drug product.
Compliance with Labeling Requirements:
Drug product labeling is another critical area for regulatory compliance. Drug product labeling must include information about the drug product, including its indications, dosage, contraindications, and side effects. The labeling must be accurate and easy to understand.
Regulatory agencies review drug product labeling to ensure that it is clear and accurate. Failure to comply with labeling requirements can result in the rejection of a drug product submission or the withdrawal of a product from the market.
The Consequences of Non-Compliance:
The consequences of non-compliance with regulatory requirements can be severe. Failure to comply with regulatory requirements can result in the rejection of a drug product submission or the withdrawal of a product from the market. These outcomes can be costly and time-consuming for manufacturers.
In addition to the financial consequences, non-compliance with regulatory requirements can also damage the reputation of the manufacturer. A product that is rejected by regulatory agencies or withdrawn from the market due to non-compliance can damage the manufacturer’s credibility and lead to a loss of consumer confidence.
Conclusion:
Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for the successful approval of drug products by regulatory agencies. Regulatory agencies have established guidelines and regulations that manufacturers must follow when developing drug products. Compliance with these guidelines is critical for the approval of a drug product.
The consequences of non-compliance with regulatory requirements can be severe. Failure to comply with regulatory requirements can result in the rejection of a drug product submission or the withdrawal of a product from the market. These outcomes can be costly and time-consuming for manufacturers and can damage the manufacturer’s reputation. Therefore, compliance with regulatory requirements should be a top priority for manufacturers developing drug products.
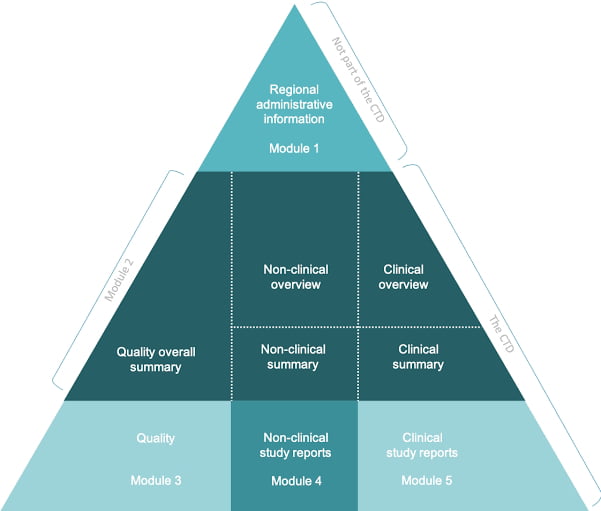
Content of Drug products submission to regulatory
When submitting a drug product to regulatory agencies for approval, the submission must include a variety of information and data to support the safety, efficacy, and quality of the product. The specific content of a drug product submission may vary depending on the regulatory agency, but generally, it includes the following components:
Cover letter: The cover letter provides a summary of the submission and includes contact information for the applicant.
Table of contents: A table of contents provides a roadmap for the submission and helps the regulatory agency navigate through the information provided.
Quality overall summary (QOS): The QOS provides a summary of the quality data for the drug product, including information on manufacturing processes, stability testing, and specifications.
Nonclinical overview and summary: The nonclinical overview and summary provide an overview of the nonclinical studies performed on the drug product, including animal studies and pharmacology studies.
Clinical overview and summary: The clinical overview and summary provide an overview of the clinical studies performed on the drug product, including information on the study design, patient populations, and results.
Clinical study reports (CSR): The CSR includes detailed information on the clinical studies performed on the drug product, including protocols, statistical analysis plans, and results.
Safety update report (SUR): The SUR provides an update on the safety profile of the drug product based on data from ongoing clinical studies or post-marketing surveillance.
Module 2 summaries: Module 2 summaries provide additional information on the drug product, including information on drug substance, drug product, and pharmaceutical development.
Labeling: The labeling provides information on the drug product, including indications, dosage, administration, and warnings.
Environmental risk assessment (ERA): The ERA provides information on the potential impact of the drug product on the environment.
Other supporting information: The submission may also include additional supporting information, such as literature references or information on the regulatory status of the drug product in other countries.
In addition to the components listed above, the submission may also include other information requested by the regulatory agency. It is essential to follow the guidelines and requirements provided by the regulatory agency to ensure that the submission is complete and meets the necessary standards for approval.
Overall, the content of a drug product submission to regulatory agencies is extensive and requires a significant amount of data and information to support the safety, efficacy, and quality of the drug product. It is crucial to work closely with regulatory agencies and follow their guidelines to ensure that the submission is complete, accurate, and meets the necessary requirements for approval.
Content of Drug products module 3
Module 3 of a drug product submission is a critical section that provides information on the quality, safety, and efficacy of the drug product. It includes the following parts:
Quality Overall Summary (QOS): The QOS provides a summary of the quality data for the drug product, including information on manufacturing processes, specifications, and analytical methods used to assess the product’s quality. It also includes information on the control strategy for the product, which outlines the critical quality attributes that must be controlled to ensure the product’s quality and consistency.
Drug Substance (Module 3.2.S): This section provides detailed information on the drug substance, including its identity, purity, and potency. It includes information on the synthetic route used to manufacture the drug substance, as well as the analytical methods used to assess its quality. It also includes information on the impurities and degradation products that may be present in the drug substance and how they are controlled.
Drug Product (Module 3.2.P): This section provides detailed information on the drug product, including its composition, formulation, and manufacturing process. It includes information on the packaging, labeling, and storage conditions for the product, as well as the analytical methods used to assess its quality. It also includes information on the specifications for the drug product, such as its appearance, potency, and stability.
Pharmaceutical Development (Module 3.2.R): This section provides information on the pharmaceutical development of the drug product, including the rationale for the selection of the formulation and the manufacturing process. It includes information on the development studies performed to assess the product’s quality, such as the selection of excipients, the optimization of the manufacturing process, and the stability studies performed to assess the product’s shelf life.
Nonclinical Overview and Summary (Module 3.4): This section provides an overview of the nonclinical studies performed on the drug product, including information on the study design, animal species, and results. It also includes information on the toxicology studies performed to assess the safety of the drug product.
Clinical Overview and Summary (Module 3.5): This section provides an overview of the clinical studies performed on the drug product, including information on the study design, patient populations, and results. It includes information on the safety and efficacy of the drug product, as well as any adverse events observed in the clinical studies.
Module 3 of a drug product submission provides detailed information on the quality, safety, and efficacy of the drug product. It is a critical component of the submission and requires a significant amount of data and information to support the product’s approval. It is crucial to work closely with regulatory agencies and follow their guidelines to ensure that the Module 3 submission is complete, accurate, and meets the necessary requirements for approval.